Content

Bad debt expense is reported within the selling, general, and administrative expense section of the income statement. However, the entries to record this bad debt expense may be spread throughout a set of financial statements. The allowance for doubtful accounts resides on the balance sheet as a contra asset. Meanwhile, any bad debts that are directly written off reduce the accounts receivable balance on the balance sheet. Many businesses use a more refined version of the percentage-of-receivables approach, known as the Aging of receivables approach.
Graeme Watt on bad debt worries, vendor downsizing and how he is … – CRN UK
Graeme Watt on bad debt worries, vendor downsizing and how he is ….
Posted: Mon, 30 Jan 2023 14:33:48 GMT [source]
GAAP since the expense is recognized in a different period as when the revenue was earned. To reverse the account, debit your Accounts Receivable account and credit your Allowance for Doubtful https://online-accounting.net/ Accounts for the amount paid. When operational inefficiencies such as strikes, lockout, disruption in production, etc. are experienced by the customers, resulting in financial difficulties.
Allowance for doubtful accounts journal entry
The term bad debt can also be used to describe debts that are taken to pay for goods that don’t appreciate. In other words, bad debt is a form of borrowing that doesn’t help your bottom line.
With this approach, accounts receivable is organised into categories by length of time outstanding, and an uncollectible percentage is assigned to each category. For example, a category might consist of accounts receivable that is 1–30 days past due and is assigned an uncollectible percentage of 3%. The final point relates to businesses with very little exposure to the possibility of bad debts, typically, entities that rarely offer credit to its customers. Assuming that credit is not a significant component of its sales, these sellers can also use the direct write-off method.
Developing Organizational Provisioning Standards
A contra account is an asset account that is used to offset a parent account – in this case, the accounts receivable. As Bad Debts is not a part of sundry debtors and so it is not shown in the balance sheet of the firm. Oppositely, Doubtful Debts are a part of sundry debtors for the purpose of creation of the balance sheet, and provision for doubtful debts appears as a deduction from sundry debtors. If out of the total sum due, a certain percentage of the sum is not recovered due to non-payment, and the amount due from debtors is called debt. Bad Debt refers to the sum due from the debtors, which remains unrealized, and so they are written off in the company’s books of accounts. As against, doubtful debts refer to the debt, with which there is an uncertainty, as to the degree to which amount will be recovered from the debtor.
- Bad Debt refers to the amount which a customer owes to the firm, whose likelihood of recovery is remote as it turns out as irrecoverable.
- In either case, bad debt represents a reduction in net income, so in many ways, bad debt has characteristics of both an expense and a loss account.
- It creates a credit memo for $1,500, which reduces the accounts receivable account by $1,500 and the allowance for doubtful accounts by $1,500.
- A significant amount of bad debt expenses can change the way potential investors and company executives view the health of a company.
- Based on previous experience, 1% of AR less than 30 days old will not be collectible and 4% of AR at least 30 days old will be uncollectible.
- Therefore, when bad or doubtful debts are incurred by the firm, these are written off from the provision maintained.
In that case, the allowance for doubtful accounts will be debited, and accounts receivable will be credited. However, the net AR doesn’t get affected, and only the remaining allowance reduces from $15,000 to $5,000. Accounts receivable aging is a more precise method to calculate the allowance for doubtful accounts.
Estimating the Bad Debt Expense
Adjust the Allowance for Bad Debts account to the balance calculated in step . GoCardless is authorised by the Financial Conduct Authority under the Payment Services Regulations 2017, registration number , for the provision of payment services. A Finance Professional specializing in the areas of Credit Management, Payment Processing, Collections and Accounts Receivable. Possessing over 20 years’ experience in the field managing large global teams with a strong focus on improving efficiency within the Order to Cash cycle.
- The direct write-off method is used in the U.S. for income tax purposes.
- The understanding is that the couple will make payments each month toward the principal borrowed, plus interest.
- The Internal Revenue Service allows businesses to write off bad debt on Schedule C of tax Form 1040 if they previously reported it as income.
- Bad debt is some account receivable accounts in a business that will not be paid by the debtors, and it needs to be written off in the coming future….
- However, the jump from $718 million in 2019 to $1.1 billion in 2022 would have resulted in a roughly $400 million bad debt expense to reconcile the allowance to its new estimate.
Thus, when ABC recognizes the actual bad debt, there is no impact on the income statement – only a reduction of the accounts receivable and allowance for doubtful accounts line items in the balance sheet . For example, say a company lists 100 customers who purchase on credit and the total amount owed is $1,000,000.
In fact, the amount of such debts is based upon the firm’s evaluation & judgment. Harold Averkamp has worked as a university accounting instructor, accountant, and consultant for more than 25 years. Doubtful Debt refers to that portion of debt whose recovery is not certain. Therefore, for such debts, there is a possibility that the firm may face losses in the future. When the customer is dishonest, wherein the party has received goods on credit having no intention to discharge the debt.
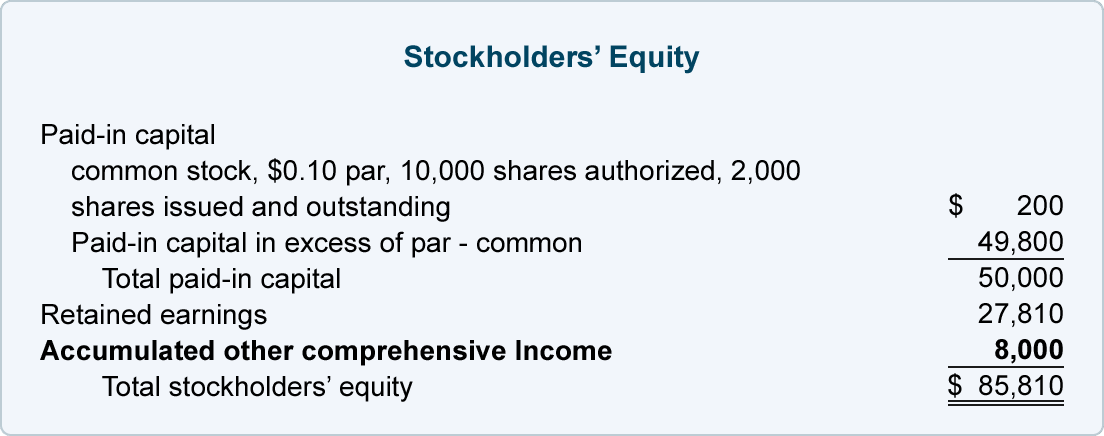
The problem with this accounts receivable balance is there is no guarantee the company will collect the payment. For many different The difference between bad debt and doubtful debt reasons, a company may be entitled to receiving money for a credit sale but may never actually receive those funds.

